The kitchen is often the busiest room in the house, and we spend a significant amount of time there preparing meals, cleaning up, and socializing. Poor kitchen ergonomics can lead to discomfort, fatigue, and even long-term health problems like back pain, neck strain, and repetitive stress injuries. Ergonomic kitchen design focuses on creating a workspace that is comfortable, efficient, and safe for the user. This article provides practical tips and expert advice to help you design an ergonomic kitchen that works for you, not against you.
Understanding Kitchen Ergonomics: What’s the Goal?
The primary goal of ergonomic kitchen design is to minimize physical strain and maximize efficiency by:
- Reducing Unnecessary Movement: Optimizing the layout to minimize walking, reaching, and bending.
- Promoting Good Posture: Designing the space to encourage proper posture while working.
- Adapting to Individual Needs: Considering the user’s height, reach, and physical capabilities.
- Improving Accessibility: Making the kitchen usable for people of all ages and abilities.
- Enhancing Comfort: Creating a workspace that is pleasant and comfortable to use.
Key Principles of Ergonomic Kitchen Design
Let’s break down the key areas to consider:
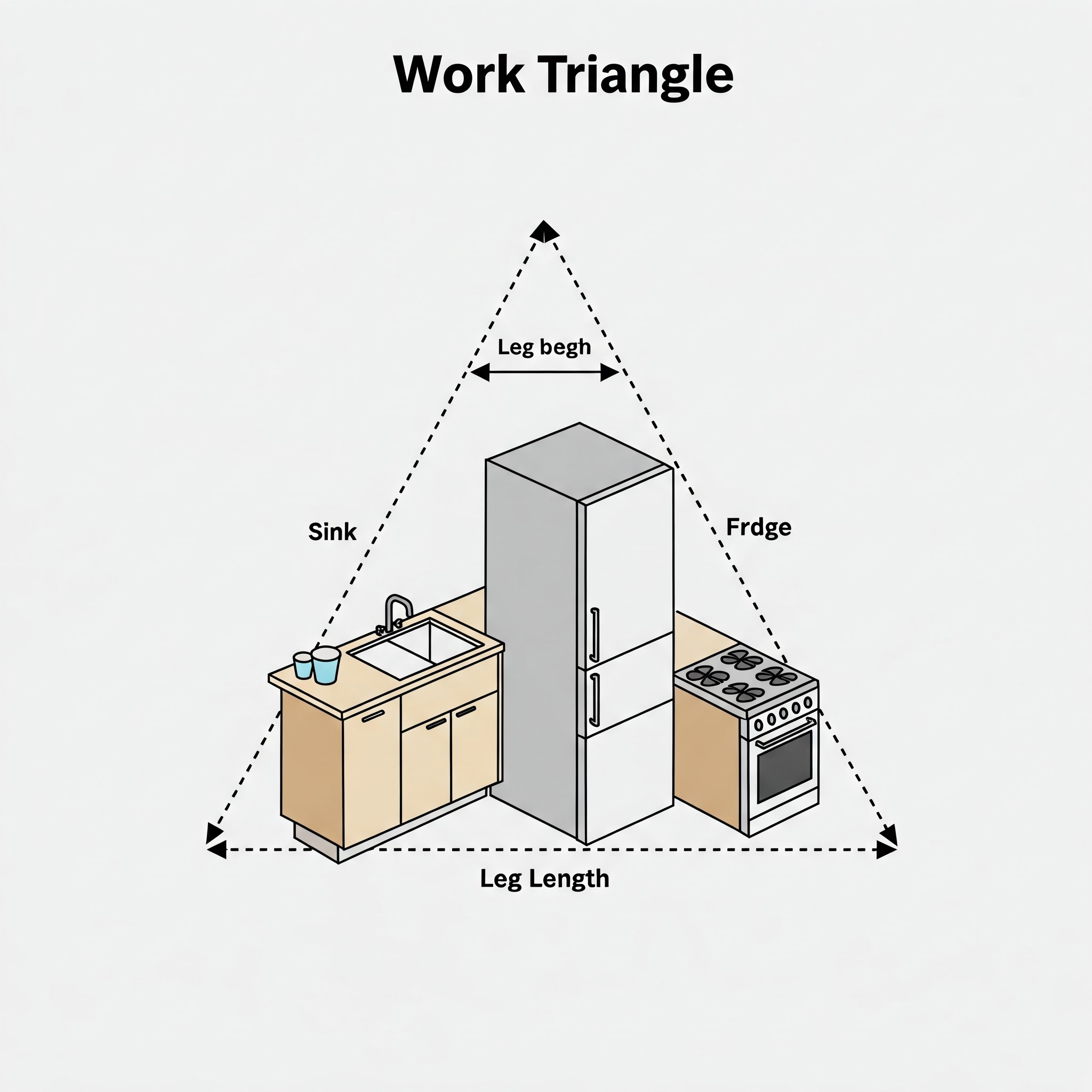
1. The Work Triangle
The work triangle is a fundamental concept in kitchen design. It connects the three primary work areas:
- The Sink (Cleaning Zone):
- The Cooktop/Oven (Cooking Zone):
- The Refrigerator (Storage Zone):
Ergonomic Guidelines:
- Ideal Triangle Sum: The total distance between these three points should ideally be between 12 and 26 feet.
- Leg Lengths: Each leg of the triangle (the distance between two points) should be between 4 and 9 feet.
- No Obstructions: The triangle should not be obstructed by islands, peninsulas, or other obstacles.
- Consider Multiple Users: If multiple people cook in the kitchen, consider creating multiple work triangles or expanding the primary triangle.
2. Countertop Heights
Standard countertop height (36 inches) isn’t ideal for everyone. The optimal height depends on the user’s height and the task being performed.
Ergonomic Guidelines:
- General Rule: The countertop should be about 2 inches below your elbow when your arms are bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Varying Heights: Consider incorporating different countertop heights for different tasks:
- Lower Height (30-34 inches): Ideal for chopping vegetables or kneading dough (allows for more leverage).
- Standard Height (36 inches): Suitable for general food preparation.
- Higher Height (42-48 inches): Good for a bar area or for tasks that require less bending (e.g., washing dishes).
- Adjustable-Height Countertops: The ultimate ergonomic solution, allowing you to customize the height for different tasks and users.
3. Cabinet Placement and Accessibility
- Reach Zones: Consider the “reach zone” when planning cabinet placement. Frequently used items should be stored within easy reach (between shoulder and hip height).
- Upper Cabinets:
- Height: The bottom shelf of upper cabinets should be about 18-20 inches above the countertop.
- Depth: Avoid overly deep upper cabinets, as it can be difficult to reach items at the back.
- Pull-Down Shelves: Consider installing pull-down shelves in upper cabinets to make it easier to access items.
- Lower Cabinets:
- Drawers: Drawers are generally more ergonomic than shelves in lower cabinets, as they allow you to see and access everything without bending down.
- Pull-Out Shelves: Another excellent option for improving accessibility in lower cabinets.
- Lazy Susans: Essential for corner cabinets.
- Open Shelving: Can be ergonomic for frequently used items, but be mindful of dust and clutter.
4. Lighting
Good lighting is crucial for both safety and comfort in the kitchen.
Ergonomic Guidelines:
- Layered Lighting: Combine ambient, task, and accent lighting.
- Task Lighting: Provide bright, focused light over work areas like the sink, cooktop, and countertops. Under-cabinet lighting is essential.
- Avoid Glare: Position lights to minimize glare and shadows.
- Natural Light: Maximize natural light whenever possible.
5. Flooring
The right flooring can reduce fatigue and improve comfort.
Ergonomic Guidelines:
- Cushioned Flooring: Choose flooring materials that offer some cushioning, such as cork, rubber, or wood.
- Anti-Fatigue Mats: Place anti-fatigue mats in front of the sink, cooktop, and other areas where you stand for long periods.
- Avoid Hard, Unforgiving Surfaces: Materials like concrete and ceramic tile can be hard on the feet and back.
6. Appliance Placement
- Dishwasher: Ideally located next to the sink for easy loading and unloading. Consider raising the dishwasher slightly to reduce bending.
- Oven: Wall ovens are generally more ergonomic than range ovens, as they allow you to access the oven without bending down. Consider a side-opening oven for even better accessibility.
- Microwave: Place the microwave at a comfortable height, ideally between countertop and shoulder height. Avoid placing it above the cooktop, as this can be awkward and potentially dangerous.
- Refrigerator: Consider the work triangle when placing the refrigerator.
7. Storage Solutions
- Vertical Storage: Maximize vertical space with tall cabinets, shelves, and wall-mounted organizers.
- Pull-Outs and Drawers: Make it easier to access items in deep cabinets.
- Lazy Susans: Ideal for corner cabinets.
- Clear Containers: Use clear containers to easily see what’s inside.
- Label Everything: Label containers and shelves to stay organized.
8. Ergonomic Tools and Accessories
- Comfortable Knives: Choose knives with ergonomic handles that fit your hand comfortably.
- Adjustable-Height Stools: Provide seating that can be adjusted to different countertop heights.
- Step Stools: Make it easier to reach items in high cabinets.
- Pot Fillers: A faucet located near the cooktop that eliminates the need to carry heavy pots of water from the sink.
9. Universal Design Considerations
Universal design principles make the kitchen accessible and usable for people of all ages and abilities:
- Wider Doorways and Hallways: Allow for wheelchair access.
- Roll-Under Sinks and Cooktops: Provide knee space for seated users.
- Lever Handles: Easier to operate than knobs.
- Contrasting Colors: Help people with visual impairments distinguish between different surfaces.
- Adjustable-Height Features: Allow for customization to individual needs.
Conclusion
Ergonomic kitchen design is an investment in your comfort, health, and well-being. By implementing these tips, you can create a kitchen that is not only beautiful but also a pleasure to work in. Remember to consider your individual needs and preferences, and don’t be afraid to seek professional advice from a kitchen designer or occupational therapist.






Leave a Comment